The Anaerobic Threshold
The anaerobic threshold is defined as the power at which a maximum steady-state of lactate production and lactate clearance occurs. At this point, the lactate concentration in the blood reaches a steady state and remains constant. The higher the power at the anaerobic threshold, the better the endurance performance of an athlete.
In simple terms, the anaerobic threshold describes the highest intensity that can be maintained as a continuous power output over a longer period of 40 to 70 minutes.
The Anaerobic Threshold Explained
To understand the anaerobic threshold, let's consider the two energy-producing systems in the human body. The aerobic- (with oxygen) and anaerobic (without oxygen) system. The aerobic system metabolizes fats and carbohydrates to produce the body's own form of energy - ATP. The metric to assess aerobic metabolism is maximal oxygen uptake (VO2max). The anaerobic system, on the other hand, almost exclusively metabolizes carbohydrates for energy supply.
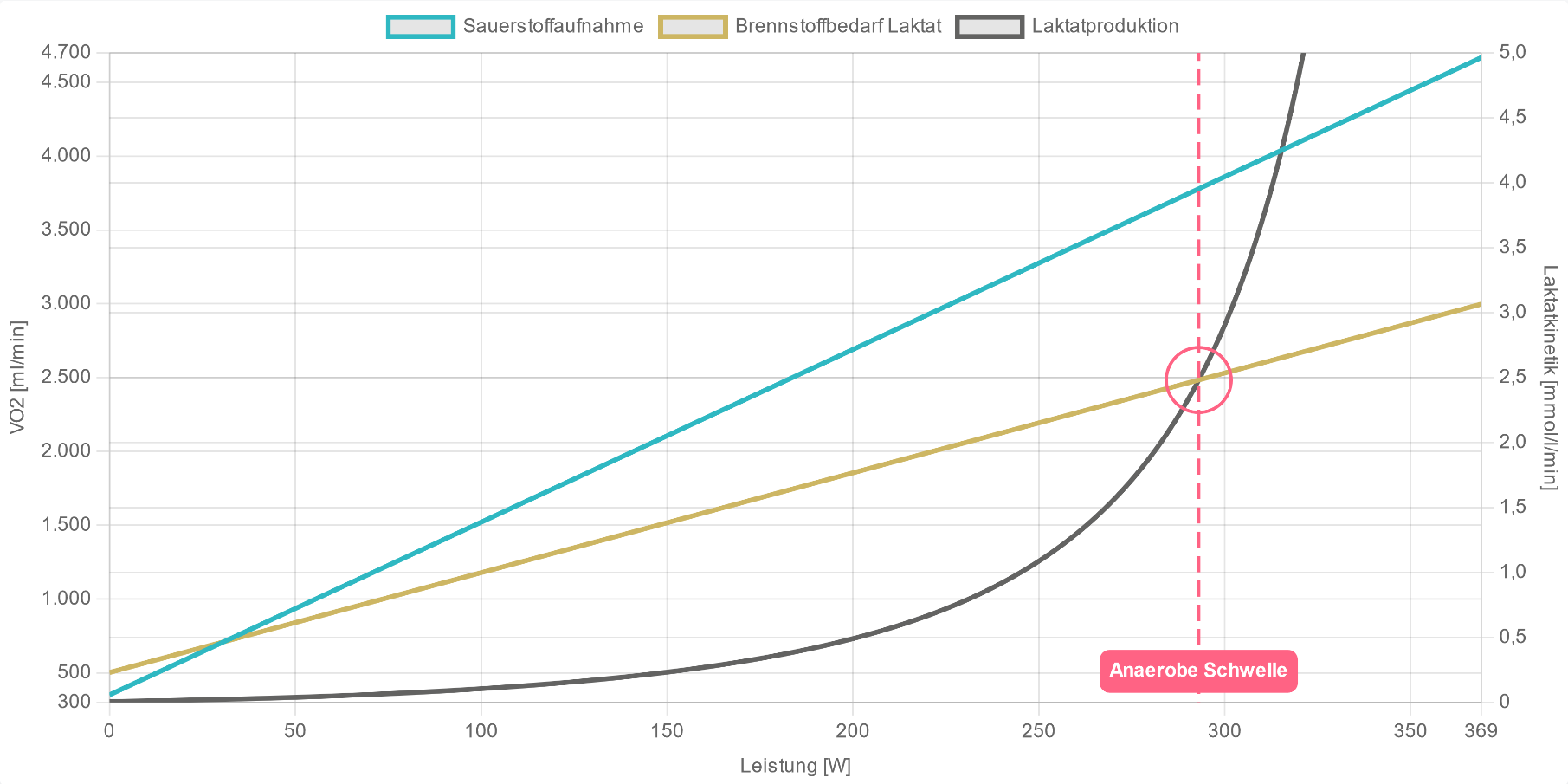
Oxygen uptake rises about linearly with increasing exercise intensity, and it takes approximately 12 milliliters of oxygen per minute for one watt of applied power to the pedal. The anaerobic system (glycolytic metabolism) produces lactate and is described by the parameter of maximum lactate production rate (VLamax). Anaerobic metabolism refers to processes of energy production that occur without oxygen. In contrast to the aerobic system, lactate production proceeds exponentially with increasing load.
The intersection of the two systems represents the steady state of lactate production and lactate clearance, which can be measured in the blood.
The two systems of energy production, therefore, differ not only in their capacity and performance but also in their profile. To increase the anaerobic threshold, the energy supply and the contribution of the two metabolic pathways can be trained.
Metabolism diagram of an exemplary AI DIAGNOSTICS performance report
Training to Improve the Anaerobic Threshold Performance
To understand how you improve the anaerobic threshold performance through training, it helps to look at the AI DIAGNOSTICS analysis graph. It's about moving the intersection of the two systems to the top right by:
- improving the linearly increasing aerobic system (VO2max)
- reducing the exponentially increasing, anaerobic lactic system (VLamax)
Therefore, if you want to understand the composition of your individual anaerobic threshold, you need to know your VO2max and VLamax. Through effective training with exact and individual training zones, both systems can be trained simultaneously. Often one system is better developed than the other, and only those who know their individual metabolic profile can optimize their training program.
For long, steady endurance efforts like a long-distance triathlon or a cycling Gran Fondo, the ideal profile shows high aerobic capacity (VO2max) and low anaerobic capacity (VLamax). This means that fewer carbohydrates are metabolized for energy production and less lactate is produced. At the same time, a high oxygen uptake allows for a high rate of fat metabolism as well as an improved capacity to break down lactate. As a result, the lactate steady state occurs at higher intensities and the intersection in the graph above shifts to the right.
For more information on anaerobic threshold training, click here:
What Limits the Duration of Exercise at the Anaerobic Threshold?
When carbohydrate stores are full, sustained performance at the anaerobic threshold can be maintained for approximately 40 to 70 minutes. Fatigue depends on many factors, but an important limiting factor of exercise duration is the limited amount of stored glycogen.
Performance in the anaerobic threshold range requires high energy and carbohydrate consumption. Even a high intake of exogenous carbohydrates cannot fully compensate for carbohydrate expenditure, eventually resulting in a depletion of glycogen stores and a drop in performance.
AI DIAGNOSTICS determines the individual carbohydrate expenditure, and the included Carbohydrate Manager determines the amount of available glycogen.
Why Should I Know My Anaerobic Threshold?
The individual anaerobic threshold describes the maximum continuous power in endurance sports and is one of the most important determinants of endurance performance.
In most racing scenarios, performance is above the anaerobic threshold (i.e., race-deciding moments in a bike race) or below (i.e., steady pacing in a long-distance triathlon or Gran Fondo). Only in a steady time trial over 40 to 60 minutes and shorter triathlons, the anaerobic threshold represents continuous race intensity. Still, the higher your anaerobic threshold, the higher your relative race performance in your next bike race or triathlon.
Knowing exactly where your anaerobic threshold is and how it is physiologically composed is a fundamental requirement for effective training.
How Does AI DIAGNOSTICS Determine My Individual Anaerobic Threshold?
AI DIAGNOSTICS determines your individual anaerobic threshold, VO2max, VLamax, Fatmax and training zones based on the performance data you have uploaded. Hundreds of data sets and physiological correlations form the basis of the AI DIAGNOSTICS method. The parameters validate each other to ensure the results are always physiologically coherent.
Why the FTP Test Is Not Enough
FTP (Functional Threshold Power) is a randomly chosen metric that has little physiological background. It claims to describe the highest possible power output over an exercise duration of 60 minutes. The classic method for determining FTP, a 20-minute FTP test, usually overestimates the 60-minute power output. The training zones derived based on FTP are too intense and do not provide the desired training adaptations.
Additionally, FTP does not provide any information about how the power is composed. FTP and anaerobic threshold both describe continuous power, but they are just numbers without context. To effectively direct training, you need to understand how power is composed. By looking at aerobic and anaerobic metabolism in a differentiated way, AI DIAGNOSTICS offers a significant advantage over the FTP test.
What Is a Good Anaerobic Threshold?
Classification of performance at the anaerobic threshold depends on age, gender, training volume, and environmental conditions. For comparability, absolute performance is related to body weight and is described as the "relative anaerobic threshold." For a 75 kg athlete with an absolute threshold power of 300 watts, this results in 4 watts per kilogram (w/kg) of relative threshold power.
Reference of Anaerobic Threshold Power
The anaerobic threshold is not a fixed number but describes a range that shifts depending on fatigue, carbohydrate availability, altitude exposure and climatic conditions. In order to hit the right training intensity, set up an individual pacing strategy or monitor performance development, a performance diagnostic should be performed.
What Happens above the Anaerobic Threshold?
If the power output exceeds the anaerobic threshold, the steady state of lactate production and lactate combustion in the body can no longer be maintained - the lactate concentration in the blood increases. The energy demand continues to increase and lactate production can no longer be compensated under increased oxygen demand. An increased energy supply by the anaerobic system leads to an accumulation of lactate and released H+ ions, lowering the pH value of the blood (acidosis).
Below the anaerobic threshold, however, the oxygen uptake capacity of the muscles is sufficient to continue metabolizing the accumulated lactate during exercise.
Overview of “Threshold” Synonyms
Athletes, sports scientists, and sports medicine specialists use multiple synonyms for the term anaerobic threshold such as "FTP", "aerobic threshold", "aerobic-anaerobic threshold", "LT2", "lactate threshold", "maximal lactate steady state (MLSS)" or "critical power".